Side Effect: Cough
What is a cough?
A cough begins with an irritation in the throat or lungs. The purpose of a cough is to try to expel, or get rid of, any foreign particles and restore air flow into and throughout the lungs.
What does coughing look like?
Depending upon the the cause of the cough, it may look and feel differently. For example, a cough caused by a medication known as an ACE inhibitor usually presents as a persistent dry cough, whereas an infection may cause fluid accumulation in the lung and sound more like a wet cough. If there is ever concern about your ability to breathe, you should call emergency services, go to your nearest emergency department, or see your doctor right away.
Cough
Click to enlarge
The development of a sudden or persistent cough is reason to call your doctor right away to determine the cause and appropriate treatment
Who gets a cough?
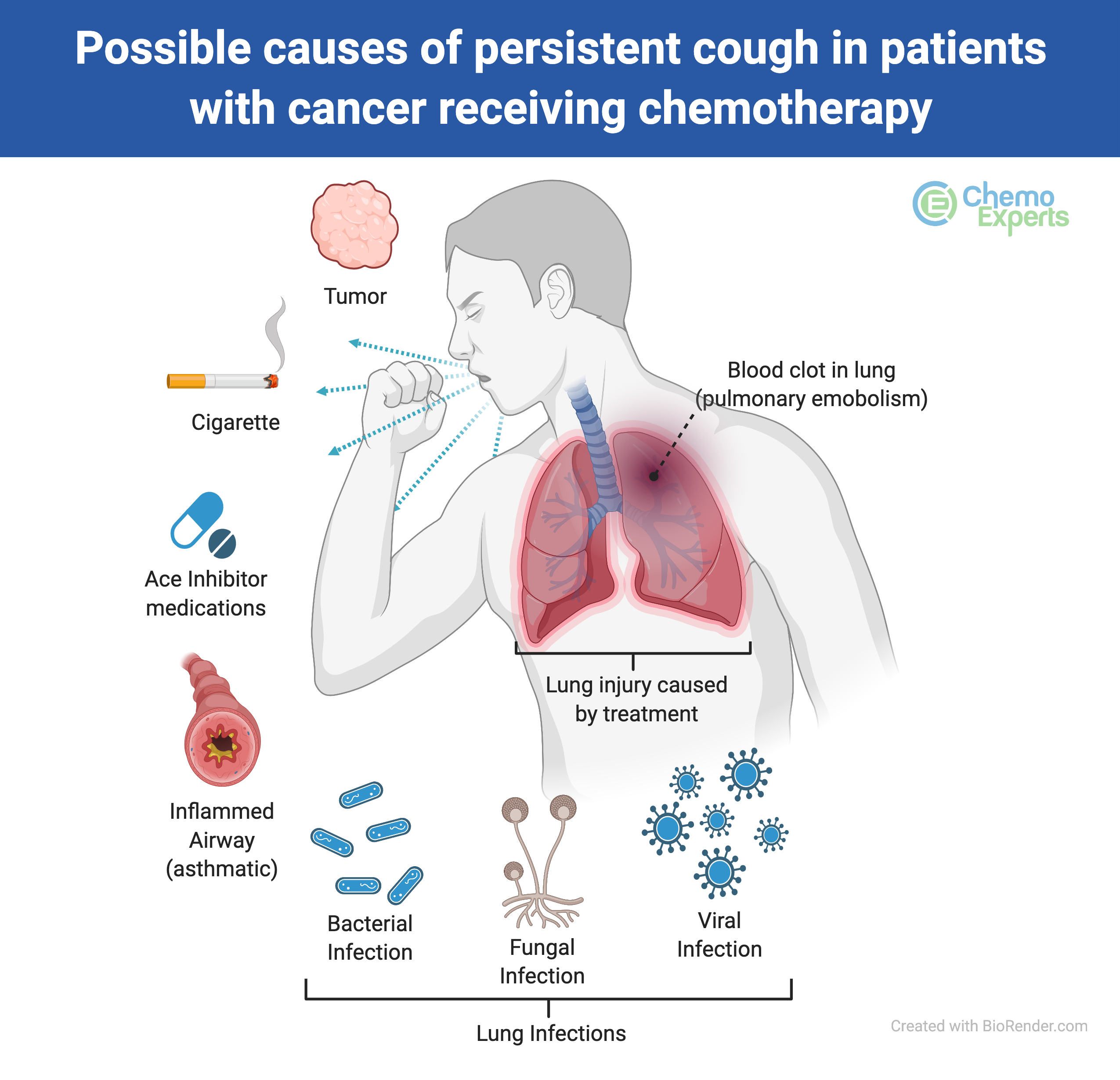
If you suddenly develop a cough, it is important to determine if it requires immediate medical attention. For example, a blood clot in the lung, or certain types of lung infections can be life-threatening and should be addressed as soon as possible.
There are many other possible causes for coughing, such as:
- Smoking or vaping
- Polluted air
- Tumor in the lung
- Certain medications, such as ACE inhibitors:
- Lisinopril
- Benazepril
- Captopril
- Medications that cause cough via an unknown mechanism
- Medications that cause inflammation of the lungs
- Medications that cause fluid build-up around the lungs:
How long can coughing last?
The duration of coughing depends entirely upon the cause and the abiiity to identify the cause and treat it. For example:
- If caused by medication, the cough may not go away until the medication is no longer taken and its effects wear off
- If caused by infection, the cough may not go away until the infection is adequately treated or eliminated by your immune system
How do you prevent a cough?
Underlying conditions, such as asthma, or seasonal allergies are common causes of cough that may be preventable with medications. The best way to prevent a cough is to avoid triggers whenever possible.
To prevent infectious causes of a cough, some patients may qualify to receive preventative medications based upon the chemotherapy treatment they receive. This type of antimicrobial therapy is often referred to as "prophy," or prophylaxis.
- Whenever applicable, we have tried to specify when patients may qualify for prophy medications on each individual treatment regimen page.
- Please see the treatment regimen page for specifics on antimicrobial (eg. antibiotic, antiviral, and antifungal) prophylaxis.
How do you treat a cough?
- If the cough is due to a medication, the medication should be switched to an alternative agent when possible.
- If the cough is due to an infection, it will be important for your doctor to determine what is causing it so that the proper treatment can be prescribed.
- If the cough is due to a smoking, resources are available through your doctor to help you stop smoking
- If the cough is due to a cancer, surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or a combination of these trreatments may be recommended depending upon the type of cancer causing the cough
If your doctor determines it is safe to take cough suppressants, the following may be recommended or prescribed:
Over-the-counter cough suppressants:
Prescription cough suppressants:
- Benzonatate (tessalon perles)
- Codeine-containing elixir
- Hydrocodone-containing elixir (reserved for people with severe pain and coughing)
Created: February 10, 2024
Updated: February 21, 2024
 +
+
 +
+